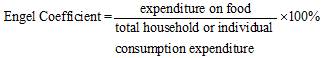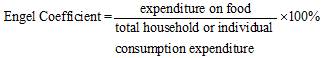
Explanatory Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
Disposable Income refers to the total income at the disposal of sampled households gained during the survey, which can be used for final consumption expenditure and savings. Disposable income includes cash and income in kind. By income source, disposable income can be divided into 4 types, namely wage income, net business income, net property income and net transfer income. The following formula is used:
Disposable Income = wage income + net business income + net property income + net transfer income
Of which: Net business income = business income - business expense - depreciation of productive fixed assets - production tax
Net property income = property income - property expenditure
Net transfer income = transfer income - transfer expenditure
Wage Income refers to all payments of labor and various welfares earned by employed persons through all channels, including all payments of labor and welfare gained from institutional or individual employers, various freelance work, part-time job, and scattered work.
Net Business Income refers to the net income of a family or family members from productive and operating activities. It is the net income of all operating income deducting business expense, depreciation of productive fixed assets and production tax. The following formula is used:
Net business income = business income - business expense - depreciation of productive fixed assets - production tax
Net Property Income refers to the net income of a family or family members earned by deducting relevant expenses from returns of their financial assets, non-financial assets (such as house) and natural resource delivered to other institutions, families or individuals for management. Net property income does not include income from premium of property ownership transfer and it shall be regarded as ¡°non-revenue proceeds¡±.
Net Transfer Income refers to net income after deducting recurrent or compulsory transfer payment of sampled households to the nation, institutions, households or individuals from various recurrent transfer payments by the nation, institutions, social groups to households and recurrent income transfer among households.
The following formula is used: Net transfer income = transfer income - transfer expenditure
Transfer Income refers to various recurrent transfer payment from the nation, institutions and social groups to households, along with recurrent income transfer among households, including retirement pension, social relief and allowance, policy production subsidiary, policy living subsidiary, disaster relief fund, recurrent donation and compensations, medical expense reimbursement, alimony income among households and income mailed or brought by non-permanent members of such household, etc. Transfer income does not include physical donation among households.
Transfer Expenditure refers to the recurrent or compulsory transfer payment made by the sampled households to the nation, institutions, households or individuals, including tax payment, various social security expenditures, alimony expenditure, recurrent donation and compensation expenditure and other recurrent transfer expenditure, etc.
Consumption Expenditure refers to total expenditures of households for consumption in daily life, including expenditures on consumer goods and services. By usage, it includes 8 categories, i.e. expenditures on food, tobacco and liquor, clothing, housing, living articles and services, transportation and communication, educational, cultural and recreational services, healthcare and medical services, and other goods and services. By source, it includes cash consumption and physical consumption (including self-produced and self-used products and those from institutions or employers, government and other social organizations).
Dependents Per Labor Force refers to the number of permanent population in the sampled household divided by the number of full/semi labor force. The following formula is used:
Dependents Per Labor Force = Number of Permanent Population in the Sampled Households / Number of Full/Semi labor force
Full/Semi Labor Force in Rural Households refers to persons among permanent family members in rural households who are capable of working and work frequently. This is one of the indicators for basic production elements, and an important source for production development and increase of farmer¡¯s household income. As stated in regulations, rural males aged 18-50 and females aged 18-45 are full labor force. Males aged 16-17 and 51-60 and females aged 16-17 and 46-55 are semi labor force. Full/Semi Labor Force in Rural Households includes the male and female full/semi labor force within the above-mentioned range age as well as those beyond such range of ages who are capable of working and work frequently; also include labor force among permanent members in rural households who are employees. But it excludes persons who are within the range of labor age but incapable of working.
Total Building Area of Current Houses refers to the total building area of house resided by the surveyed households, which is calculated on the basis of the property ownership certificate or lease certificate. The building area can also be calculated as the usable floor space multiplied by 1.333, which shall deduct the building area of the house specially used for lease.
Engel Coefficient Along with the increase in household and personal income, a gradually smaller proportion of income is used for purchase of food. This law is called Engel¡¯s law, and the coefficient reflecting such law is called Engel¡¯s Coefficient. The following formula is used: